What is EDI?
EDI is used by companies to electronically exchange business information and documents such as orders, invoices, and financial transactions with various business partners like suppliers, distributors, manufacturers, and other stakeholders.
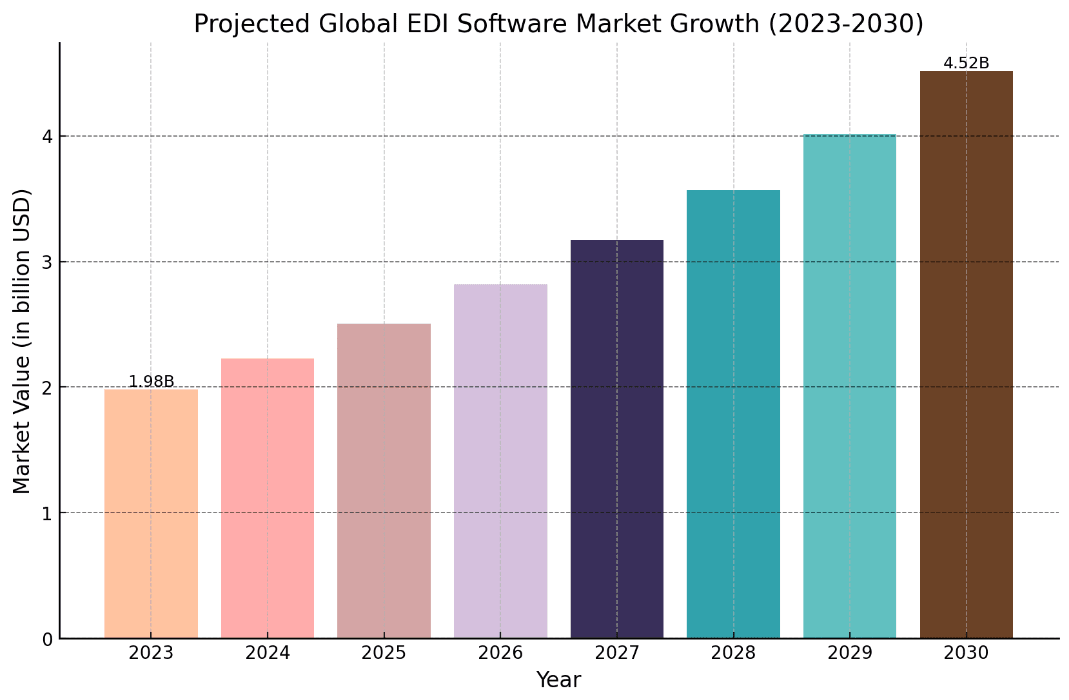
It's goal is to improve communication throughout supply chains and business networks—and it does. EDI adoption rates are through the roof, with the market set to grow at a rate of 12,5%, year over year.
What are EDI standards?
Since the data exchange happens via computer systems, the data has to be standardized so that it can travel securely, transparently and automatically.
EDI Standards are rules that define how data should be formatted and structured before being exchanged. Different industries will adhere to different EDI standards.
Some of the well-known EDI standards are:
ANSI X12 (used primarily in the United States)
UN/EDIFACT (widely used internationally)
TRADACOMS (used in the UK retail industry)
Benefits of EDI
- Productivity and efficiency - Automating EDI reduces the need for manual labor in coordinating and handling data transfers, thereby expediting business operations.
- Accuracy - EDI ensures a consistent and standardized process, reducing the risk of errors happening when humans carry out repetitive tasks
- Visibility - Exchanges can be tracked and viewed end-to-end, for regulation-ready monitoring and auditing.
- Cost savings - Focusing on electronic versions of documents means less investment is needed for physical paper, filing and storage.
- Collaboration - Different partners can connect to exchange information. This can happen either directly between two parties (peer-to-peer), or through a central system that all partners connect to.

What are EDI communication protocols?
EDI communication protocols are the various methods used to transport EDI data securely from sender to receiver. These protocols ensure data integrity and security during transmission.
Common EDI communication protocols include:
FTP (File Transfer Protocol): for secure file transfers over internet networks.
HTTP/HTTPS: used for transmitting data over the World Wide Web.
AS2, AS3, and AS4: which are standards that guide secure data exchange over the internet.
SFTP (SSH File Transfer Protocol): for secure file transfers over private networks.
For a quick into into why SFTP is considered the most secure protocol, watch the following video by Hans IT Academy.
What are the criteria for choosing an EDI protocol for your business?
In the same wayt that different industries will apply different EDI standards, unique business will opt for the EDI communication protocol that suits their needs, facilities, and setup.
There are numerous criteria involved in selection including:
1. Security
- Encryption: Does the protocol support data encryption to secure sensitive information during transmission?
- Authentication: Does it facilitate secure authentication mechanisms to prevent unauthorized access?
2. Compatibility and Interoperability
- Industry Standards: Does the protocol adhere to the standards commonly used in your industry?
- Partner Requirements: Are your business partners, suppliers, or customers using a specific protocol? You'll need a protocol that can work seamlessly with theirs.
- Integration with Existing Systems: How well can the protocol integrate with your existing IT infrastructure?
3. Reliability and Performance
- Data Integrity: Does the protocol ensure that the data is not altered during transmission?
- Error Handling: Does it have mechanisms to handle errors efficiently and guarantee message delivery?
- Speed: What is the data transmission speed of the protocol?
4. Cost and Resources
- Implementation Cost: What are the costs associated with implementing and maintaining the protocol?
- Resource Requirements: Does the protocol require significant resources to manage and maintain?
5. Technical Support and Community
- Vendor Support: Does the protocol vendor offer reliable technical support?
- Community and Documentation: Is there a community of users and comprehensive documentation to help you solve potential issues?
6. Regulatory Compliance
- Compliance with Laws: Does the protocol comply with relevant regulations and laws in your industry?
- Audit Trails: Does it support generating audit trails for compliance reporting?
7. Scalability
- Volume Handling: Can the protocol handle the volume of data your business needs to transmit?
- Growth: Can it scale to meet the growing needs of your business?

8. Functionality and Features
- Ease of Use: How user-friendly is the protocol?
- Automation: Does the protocol support automation to streamline business processes?
9. Proof of Concept and Testing
- Testing: Before finalizing a protocol, can you test it to ensure it meets your business requirements?
- Proof of Concept: Can you develop a proof of concept to understand the protocol's functioning better?
Comparing EDI communication protocols: Advantages, disadvantages & recommendations
Communication protocols are at the heart of successful EDI. It’s a question of identifying the right protocols and taking into consideration the abovementioned factors.
Navigating this doesn't need to be complicated. It's pretty much about comparing, evaluating, and learning from resources like this blog.
Now, let's check out what's out there:
AS2
AS2 (which stands for Applicability Statement 2) is an EDI communication protocol that’s been widely adopted across various industries. It is based on HTTP/S communication, with built-in support for secure message transfer such as encryption (thank you HTTPS!), digital signatures, and data integrity checks.
AS2 also offers Message Disposition Notifications (MDNs), for partners to issue receipt confirmation of successful transfers, so that you can be sure that your message has been received at the intended destination (think Whatsapp blue ticks but for business documents).
The combination of encryption with digital signatures that help verify who the sender is and that the message hasn’t been tampered with, help prevent data loss and find who is accountable for what.
Its high security and traceability is why the AS2 communication protocol is used by healthcare organizations to comply with regulations such as HIPAA, but it is also common within retail and CPG supply chains.

However, since AS2 is based on HTTPS communication, it necessitates that both partners set up an AS2 server, which could be a bit complicated in terms of implementation.
- Given that AS2 servers interact with the AS2 servers of trading partners, there needs to be a mutual agreement on several parameters.
These include message format, encoding, encryption, compression methods, and transmission options (for example, how MDNS are configured).
- AS2 relies on digital certificates for encryption and authentication. You’ll have to learn how to obtain and set up these certificates from trusted authorities, renew them periodically, and maintain a proper certificate chain.
This involves managing both your own certificates as well as those belonging to your partners.
- The AS2 server not only operates as a server (receiving HTTPS requests) but also as a client (making HTTPS requests to partner AS2 servers), making it crucial that the network infrastructure is both dependable and secure.
This means you need to guarantee appropriate connectivity, implement correct firewall rules, manage port forwarding, and so on.
AS3
AS3 is designed to work on top of FTP or FTPS for file transport. Its relative simplicity is reflected in the fact that you don’t need to control or host the FTP server if you have an AS3 client, unlike with AS2 where both parties need to open HTTP/S ports.
AS3 is primarily used with FTPS for the sake of security and has advantages over AS2 when working with large files, with built-in compression over the wire, and support for file segmentation.
This means that large files are divided into smaller segments that are transferred concurrently, with the added benefit of being able to resume interrupted transfers.
AS3 operates a client/server model, in contrast to AS2’s peer-to-peer approach. Its open standards protocol also makes AS3 suitable for organizations with multiple trading partners who are looking for high levels of interoperability.
AS3 does come with certain drawbacks:
- FTPS is known for being difficult to implement across firewalls because of the use of two ports - one (21 most of the time) for control and another random one for data.
- Given that AS3 involves partners uploading files that other partners subsequently download, AS3 is slower than AS2 synchronous communication.
File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
To this day, FTP remains one of the most popular protocols for transferring files. It’s great for large (multi-GB) file transfers and allows file upload or download resumes.
However, FTP was created back in 1971, before the public internet and in an era where digital security was non-existent. It simply wasn’t built with security in mind - all communication is sent in plain text, not encrypted at all.
You can install firewalls, but the non-secure nature of FTP means the risks from brute force attacks and spoofing remain. As noted before, FTP, just like its secure younger brother FTPS, doesn’t make it easy on firewalls with its use of two ports.
Especially because FTP uses two ports – one for commands and connections, the other for transferring data. Moreover, being a generic file transfer protocol, data verification or receipt notifications are not included in this option.
Odette File Transfer Protocol (OFTP2)
The O stands for Odette, the European automotive standards body. That’s why this protocol is common within automotive industry supply chains. Initially OFTP worked across ISDN networks, before the migration to internet-based communication.

OFTP2 is a simple file transfer protocol, accompanied with encryption, digital signatures, and compression. Transferred files can be EDI messages, such as business documents, but also any other type of data such as large CAD files (assembling a car is a complex task!).
OFTP2 is designed for uninterrupted and large-capacity transfers.
OFTP2 adoption is relatively limited, because of its industry-specific nature. All participants need OFTP2, and that often means purchasing and managing OFTP2 software. Alongside making sure the business has the necessary Odette certifications.
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3)
Amazon S3 entered the cloud market in 2006, using its early-mover advantage to achieve its current market-leading position. This includes advantages around availability (AWS say “Monthly Uptime Percentage of at least 99.99%”), data durability (“11 nines”), and scalability (“virtually unlimited”).
S3 is compliant with PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, encrypting data using AES-256 and suitable for use with many other acronyms. S3 also offers object locking for regulations that call for WORM (write once, read many) compliant storage, such as SEC and FINRA.

For region-specific legislation, such as GDPR, you can specify the region for your S3 bucket. What’s more, S3 comes with a secure access protocol based on HTTPS, to help enforce security for data in transit.
Of course, the “Amazon” part of its name tells you it’s proprietary for AWS. So if you’re on Azure or GCP, you’re probably not even reading this bit (thanks if you are, though). S3 offers an elastic pay-as-you-go model, but costs add up the more you make data access and retrieval requests.
Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
SFTP was developed as an extension of the Secure Shell (SSH), used with the Unix and Linux operating systems. However, nowadays it is bundled with any OS (yes, even Windows).
SFTP is the de facto client-server protocol choice for transferring and exchanging files securely, even across NAT and the public internet.
For a quick comparison of protocols with further insight into SFTP's advanced security features, watch the video by Sal Aurigemma below.
SFTP comes with end-to-end data encryption and uses a single port (unlike FTP and FTPS), so no need to configure extra firewall rules. This makes SFTP ideal for use with backups, disaster recovery, and sharing files and data with 3rd parties.
SFTP is also easily automated using command line applications, while authentication is possible using not only passwords but also with the use of public and private keys, which help identify the user who connects to the server in a more secure manner.
What are the advantages of using SFTP?
- When compared to AS2, SFTP is simpler to implement and maintain since it comes out of the box and it doesn’t use TLS certificates.
- Similarly to AS3 with its underlying FTPS, there’s no need for bi-directional communication - all parties connect to the SFTP server to upload and download files, and with SFTP, these files can be either EDI messages or any other sort of file.
- SFTP is designed for efficient and reliable file transfers, allowing for large EDI files to be transmitted quickly and accurately with features such as resumable transfers and over-the-wire compression.
Nevertheless, digital signatures or receipt notifications are not part of the SFTP protocol but they can be implemented by clients that upload a signature for each uploaded file, and upload a receipt notification file for every downloaded file.
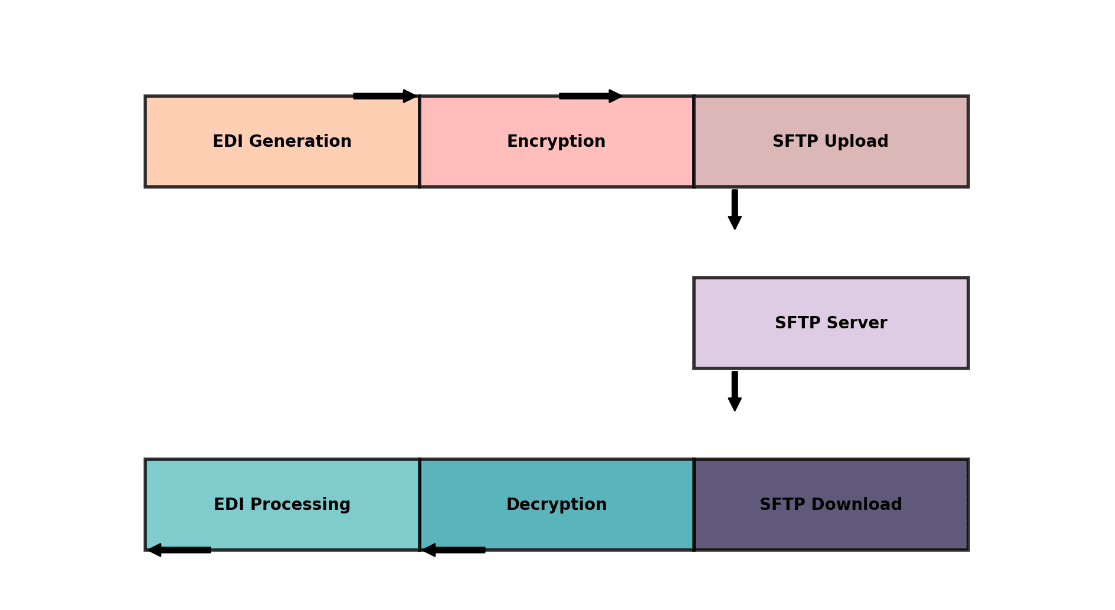
Is SFTP the right choice for you?
Ultimately, your choice of protocol involves multiple factors. These include trading partner requirements, implementation goals, and standardization/technical requirements.
When given a choice, a managed SFTP server has several benefits over AS2:
- No need to enable inbound traffic to your private network (either to the AS2 server or between the AS2 server and your other systems).
- No maintenance - no server patches, backups, certificate management or anything of that nature.
- Focus on the actual integration. Generating and processing EDI messages is enough of a headache without having to take care of the infrastructure.
Meet SFTP To Go, our secure cloud storage solution, that facilitates Amazon S3 as its durable and highly available storage layer.

You can use the popular and secure protocols SFTP and FTPS to access and manage files, in addition to a friendly user interface to manage storage and access to it along with robust APIs for automation and integration.
Webhook notification triggers allow you to process files as soon as they’re uploaded, which makes for real-time processing as fast as AS2.
When combined with enhanced security measures like inbound network rules, static IP addresses, and public key authentication, SFTP To Go becomes a powerful and cost-effective solution for file based EDI integration.
To start your SFTP To Go free trial or schedule a call with our team, click here.

Frequently asked questions
What are AS2, FTP, and HTTP/HTTPS?
AS2, FTP, and HTTP/HTTPS are protocols used in the electronic data interchange (EDI). AS2 secures data transmitted over the internet, FTP facilitates the transfer of files over a network, and HTTP/HTTPS are used for data transmission over the web, with HTTPS ensuring secure, encrypted communication.
Why is EDI communication vital for businesses?
EDI communication is essential because it enhances operational efficiency, reduces manual errors, accelerates business cycles, lowers operational costs, and facilitates regulatory compliance. It provides real-time transaction status, fostering better business relationships and informed decision-making.
How does EDI communication enhance security?
EDI communication augments security through encryption during data transmission, ensuring that sensitive information is accessible only to intended recipients. It also employs authentication procedures to verify communicating parties' identities, preventing unauthorized access.
Can small businesses afford EDI solutions?
Yes, small businesses can afford EDI solutions. Initially designed for large corporations, advancements in technology have now made EDI systems affordable for small and medium enterprises (SMEs), with cloud-based EDI solutions offering a cost-effective option.
How to implement EDI communication?
To implement EDI communication in your business, follow these steps:
- Analysis: Assess your business needs and current processes.
- Selection: Choose the right EDI solution and communication protocol.
- Integration: Integrate the EDI system with existing business applications.
- Testing: Conduct tests to ensure system compatibility with business partners.
- Deployment: Roll out the EDI system organization-wide and train staff on its use.
Effects of EDI communication on supplier & customer relationships?
EDI communication positively affects supplier and customer relationships by reducing errors, speeding up transaction processes, and providing real-time updates on transaction statuses. It leads to improved accuracy, faster deliveries, and enhanced trust and collaboration between business partners.
Environmental benefits of EDI communication?
EDI communication contributes to environmental conservation by reducing paper usage and the associated waste. It also decreases the need for physical storage space and transportation of paper documents, thereby reducing a business's carbon footprint.
How to choose the right EDI communication protocol?
Choosing the right EDI protocol involves considering various factors including the nature of your business, the volume of transactions, security requirements, and your business partners' preferences. It is advisable to assess your organization's technical capabilities and to consider the cost implications before settling on a specific protocol. Consulting with an EDI expert can also aid in making an informed decision.
What are the different types of EDI communication protocols?
There are several EDI communication protocols including:
- AS2 (Applicability Statement 2): A secure data transfer protocol over the internet.
- FTP (File Transfer Protocol): Used for transferring files over a network.
- SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol): A secure version of FTP, encrypting data during transfer.
- HTTP and HTTPS: Used for transmitting data over the web, with HTTPS offering secure, encrypted communication.
- EDI over VAN (Value-Added Network): A private network provider facilitating EDI transactions between companies.